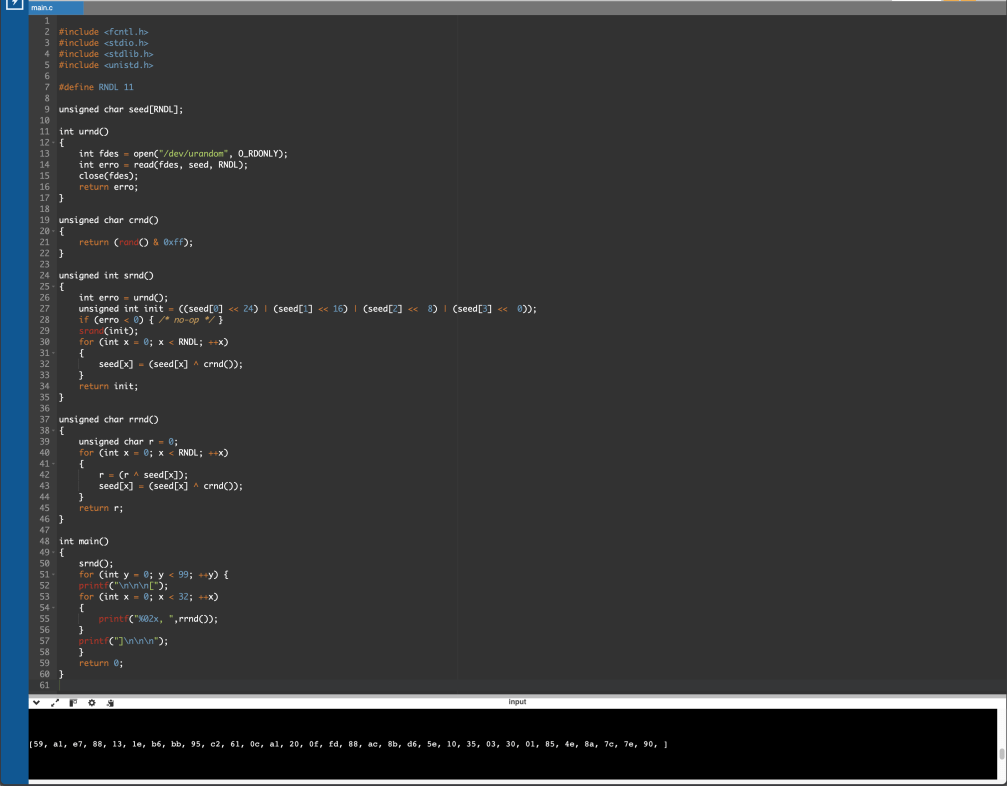
This example code will first load in 88-bits worth of /dev/urandom data into an initial seed variable which will then feed the first 32-bits into the srand() algorithm seed. Then the regular rand() function can be used to mix in the generated random data into the seeded random data to create a new stream of random output data to be used by the application.
- Comment
- Reblog
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.