With this network-wide layer-4 forward-proxy service running a bit better now, I had originally implemented a highly-modified version of the ARC4 symmetric stream cipher with a keyed checksum hashing method to work together. The one part I was missing was an EC asymmetric cipher to help protect a Diffie–Hellman based ephemeral key exchange. It’s been a number of years since I’ve experimented with this but I started an implementation using the C OpenSSL library to use a pre-generated EC key pair to protect a DH key exchange which can be used at the start of the proxy tunnel connection. You can use the openssl command to generate the EC key pair and then use this framework to load them in and perform an encrypted ECDH key exchange. As you can see below, there are a few steps needed to complete this transaction:
- The client generates an ephemeral EC key pair and encrypts the ephemeral public key with the generated public key and sends this to the server
- The server decrypts the ephemeral public key with the generated private key
- The client creates a secret number to multiply with a generated curve point and encrypts this with the generated public key and sends this to the server
- The server decrypts the clients key exchange with the generated private key and multiplies it with the server secret number to get a shared secret
- The server creates a secret number to multiply with a generated curve point and encrypts this with the ephemeral public key and sends this to the client
- The client decrypts the servers key exchange with the ephemeral private key and multiplies it with the client secret number to get a shared secret
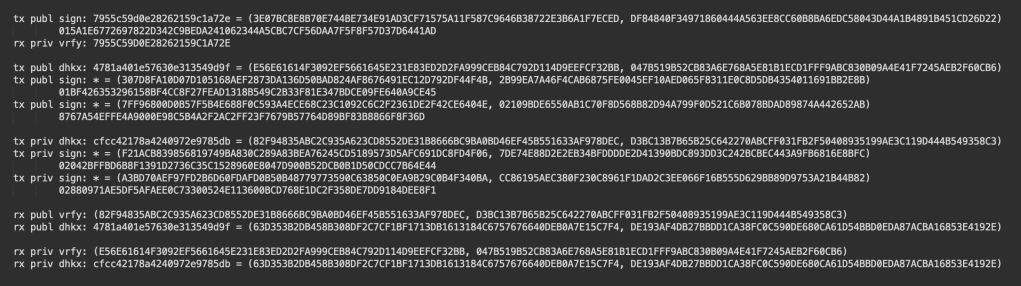
- You can see near the end there are two lines labelled “rx …. dhkx:” which contain the same shared X & Y points on the EC curve which were encrypted using the basic scheme above!
Source Code: https://github.com/stoops/eckx/tree/main
~